High-conjugation-efficiency aqueous CdSe quantum dots†
Abstract
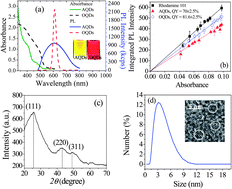
Quantum dots (QDs) are photoluminescent nanoparticles that can be directly or indirectly coupled with a receptor such as an antibody to specifically image a target biomolecule such as an antigen. Recent studies have shown that QDs can be directly made at room temperature and in an aqueous environment (AQDs) with 3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA) as the capping ligand without solvent and ligand exchange typically required by QDs made by the organic solvent routes (OQDs). In this study, we have synthesized CdSe AQDs and compared their conjugation efficiency and imaging efficacy with commercial carboxylated OQDs in HT29 colon cancer cells using a primary antibody–biotinylated secondary antibody–streptavidin (SA) sandwich. We showed that the best imaging condition for AQDs occurred when one AQD was bound with 3 ± 0.3 SA with a nominal SA/AQD ratio of 4 corresponding to an SA conjugation efficiency of 75 ± 7.5%. In comparison, for commercial CdSe–ZnS OQDs to achieve 2.7 ± 0.4 bound SAs per OQD for comparable imaging efficacy a nominal SA/OQD ratio of 80 was needed corresponding to an SA conjugation efficiency of 3.4 ± 0.5% for CdSe–ZnS OQDs. The more than 10 times better SA conjugation efficiency of the CdSe AQDs as compared to that of the CdSe–ZnS OQDs was attributed to more capping molecules on the AQD surface as a result of the direct aqueous synthesis. More capping molecules on the AQD surface also allowed the SA–AQD conjugate to be stable in cell culture medium for more than three days without losing their staining capability in a flowing cell culture medium. In contrast, SA–OQD conjugates aggregated in cell culture medium and in phosphate buffer saline solution over time.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...