Improving therapeutic effect in ovarian peritoneal carcinomatosis with honokiol nanoparticles in a thermosensitive hydrogel composite†
Abstract
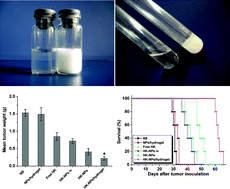
Ovarian cancer is one of the most common carcinomas and causes lots of deaths in the world. Honokiol (HK), a natural product, was proved to be a potent anti-tumor agent, however the hydrophobicity of HK limited its application. In this work, we investigated the anti-tumor efficacy of honokiol nanoparticles (HK-NPs) and honokiol nanoparticles-loaded thermosensitive hydrogel (HK-NPs/hydrogel) on ovarian cancer in vitro and in vivo. HK-NPs with small particle size and high drug loading were prepared, and HK-NPs/hydrogel with a sol–gel transition temperature at about body temperature was also obtained. In addition, HK-NPs and HK-NPs/hydrogel showed a sustained release behavior of HK in vitro. HK-NPs could effectively inhibit proliferation of SKOV3 tumor cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner and induce apoptosis of tumor cells in vitro. Furthermore, compared with controlled groups, HK-NPs and HK-NPs/hydrogel dramatically inhibited growth of tumors and prolonged the survival of mice bearing ovarian peritoneal carcinomatosis (OPC), and the effects of HK-NPs/hydrogel were more obvious than HK-NPs (P < 0.05). Intraperitoneal chemotherapy with HK-NPs/hydrogel significantly inhibited proliferation activity and angiogenesis of tumors and increased apoptosis and necrosis in tumor tissues. Therefore, our results suggested that HK-NPs/hydrogel may have great potential in clinical applications in the treatment of OPC.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...