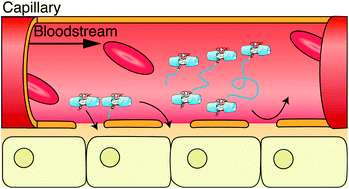
A synthetic oxygen (O2) and carbon monoxide (CO) receptor (hemoCD) composed of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-sulfonatophenyl)porphinatoiron(II) and a per-O-methylated β-cyclodextrin dimer with a pyridine linker (Py3CD) was functionalised with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) to elongate the circulation time of the receptor in the bloodstream. α-PEG monocarboxylic acid (HOOC(CH2)3(CO)O-PEG(mw)-OCH3; mw = 750 or 5k) or α,ω-PEG dicarboxylic acid (HOOC(CH2)3(CO)O-PEG(mw)-O(CO)(CH2)3COOH; mw = 10k or 20k) was reacted with the amino group of 5-(4-aminophenyl)-10,15,20-tris(4-sulfonatophenyl)porphyrin to afford a porphyrin monomer having a PEG chain or a porphyrin dimer having a PEG linker, respectively. The ferrous complexes of these PEGylated porphyrins (PEG750-, PEG5k-, PEG10k- and PEG20k-hemoCDs) bound O2 in aqueous solution, P1/2 values being 6.5–8.1 Torr at pH 7.0 and 25 °C. Each PEG(mw)-hemoCD was infused into the femoral vein of a Wistar male rat. After 6 h of the infusions, 67, 82, 86 and 42% of PEG750-, PEG5k-, PEG10k- and PEG20k-hemoCD were excreted in the urine. PEG750-hemoCD with a hydrodynamic diameter (Dh) of 3.4 nm seemed to partly leak from the blood vessels (pore size: 2–6 nm) before renal filtration (pore size: 4–14 nm). PEG5k- (Dh = 6.2 nm) and PEG10k-hemoCDs (9.0 nm) hardly passed through the blood vessels but were fully filtered by the kidney, resulting in high excretion rates. A considerable amount of PEG20k-hemoCD (Dh = 12.0 nm) was retained in the blood even at 6 h after administration. The present study demonstrates that the behaviour of hemoCD in blood after administration can be controlled by modification of hemoCD with PEG having an appropriate molecular weight.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...