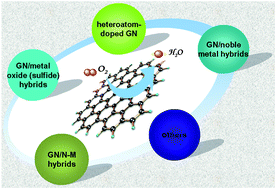
Development of state-of-the-art electrocatalysts with inexpensive and commercially available materials to facilitate sluggish cathodic oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is a key issue in the development of fuel cells and other electrochemical energy devices. Although great progress has been achieved in this area of research and development, there are still some challenges in both their ORR activity and stability. The emergence of graphene (GN) provides an excellent alternative to electrode materials and great efforts have been made to utilize GN-based nanomaterials as promising electrode materials for ORR due to the high electrical conductivity, large specific surface area, profuse interlayer structure and abounding functional groups involved. It should be noted that rational design of these GN-based nanomaterials with well-defined morphology also plays an important role in their electrochemical performance for ORR. Considerable attempts were achieved to construct a variety of heteroatom doped GN nanomaterials or GN-based nanocomposites, aiming at fully using their excellent properties in their application in ORR. In this critical review, in line with the material design and engineering, some recent advancements in the development of GN-based electrocatalysts for ORR in electrochemical energy devices (fuel cells and batteries) are then highlighted, including heteroatom-doped GN nanomaterials, GN-based nonprecious hybrid nanocomposites (GN/metal oxides, GN/N-M, GN/carbon nitride, etc.) and GN/noble metal nanocomposites.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...