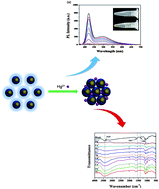
Sensitive and selective detection strategies for toxic heavy metal ions, which are rapid, cheap and applicable to environmental and biological fields, are of significant importance. As a result of specific interaction between thiol(s) used as ligands and heavy metal ions, the photoluminescence intensity of quantum dots (QDs) in PBS buffer solution was quenched and the aggregation of QDs was formed at the same time. Herein, we present water-soluble, low toxic QDs, ZnSe/ZnS, which were applied for ultrasensitive Hg2+ ion detection with a low detection limit (2.5 nM). In addition, a model has been proposed to explain the aggregation of QDs in the presence of heavy metal ions such as Hg2+ ions.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...