The bonding in thiolate protected gold nanoparticles from Au4f photoemission core level shifts
Abstract
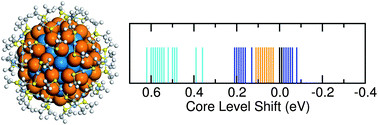
Density functional theory calculations are used to evaluate Au4f core level shifts of methyl thiolate protected Au25, Au102 and Au144
- This article is part of the themed collection: Metallic clusters

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...