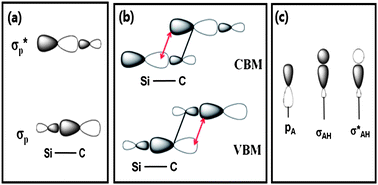
In light of the established differences between the quantum confinement effect and the electron affinities between hydrogen-passivated C and Si quantum dots, we carried out theoretical investigations on SiC quantum dots, with surfaces uniformly terminated by C–H or Si–H bonds, to explore the role of surface terminations on these two aspects. Surprisingly, it was found that the quantum confinement effect is present (or absent) in the highest occupied (or lowest unoccupied) molecular orbital of the SiC quantum dots regardless of their surface terminations. Thus, the quantum confinement effect related to the energy gap observed experimentally (Phys. Rev. Lett., 2005, 94, 026102) is contributed to by the size-dependence of the highest occupied states; the absence of quantum confinement in the lowest unoccupied states is in contrary to the usual belief based on hydrogen-passivated C quantum dots. However, the cause of the absence of the quantum confinement in C nanodots is not transferable to SiC. We propose a model that provides a clear explanation for all findings on the basis of the nearest-neighbor and next-nearest-neighbor interactions between the valence atomic p-orbital in the frontier occupied/unoccupied states. We also found that the electron affinities of the SiC quantum dots, which closely depend on the surface environments, are negative for the C–H termination and positive for the Si–H termination. The prediction of negative electron affinities in SiC quantum dots by simple C–H termination indicates a promising application for these materials in electron-emitter devices. Our model predicts that GeC quantum dots with hydrogen passivation exhibit similar features to SiC quantum dots and our study confirms the crucial role that the surface environment plays in these nanoscale systems.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...