A combined approach for the study of histone deacetylase inhibitors†
Abstract
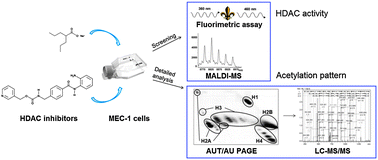
Overexpression of histone deacetylases (HDACs), with consequent hypoacetylation of histones, is reportedly associated with transcriptional repression of tumour suppressor genes. Thus, inhibition of HDACs has emerged as a promising strategy in cancer therapy. In order to monitor the effects of potential HDAC inhibitors, a multi-level approach consisting of preliminary screening (measurement of HDAC activity and semi-quantitative evaluation of histone H4 modification profile by MALDI-TOF MS) and detailed analysis of histone modification forms (using 2-D AUT/AU PAGE and LC-ESI-IT MS) has been used in this study. The data obtained provide a global insight into the effects of HDAC inhibitors on the histone acetylation status that participates in gene transcription control. Using two example inhibitors, valproic acid sodium salt and entinostat, we show that similar levels of HDAC inhibition induced by different agents can lead to distinct rates of histone hyperacetylation, suggesting that except for the direct inhibition of HDACs, additional molecular mechanisms amplifying the response are likely to be involved in the inhibitory process. The approach used in our study makes it possible not only to follow the dynamics of individual histone modification forms, but also of their combined occurrence in the N-terminal fragment.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...