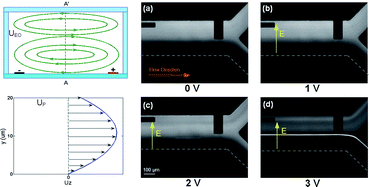
Sample pre-concentration can be a critical element to improve sensitivity of integrated microchip assays. In this work a converging Y-inlet microfluidic channel with integrated coplanar electrodes was used to investigate transverse DNA and protein migration under uniform direct current (DC) electric fields to assess the ability to concentrate a sample prior to other enzymatic modifications or capillary electrophoretic separations. Employing a pressure-driven flow to perfuse the microchannel, negatively charged samples diluted in low and high ionic strength buffers were co-infused with a receiving buffer of the same ionic strength into a main daughter channel. Experimental results demonstrated that, depending of the buffer selection, different DNA migration and accumulation dynamics were seen. Charged analytes could traverse the channel width and accumulate at the positive bias electrode in a low electroosmotic mobility, high electrophoretic mobility, high ionic strength buffer or migrated towards an equilibrium position within the channel in a high electroosmotic mobility, high electrophoretic mobility, low ionic strength buffer. The various migration behaviours are the result of a balance between the electrophoretic force and a drag force induced by a recirculating electroosmotic flow generated across the channel width due to the bounding walls. Under continuous flow conditions, DNA samples were concentrated several-fold by balancing these transverse electrokinetic forces. The electrokinetic trapping technique presented here is a simple technique which could be expanded to concentrate or separate other analytes as a preconditioning step for downstream processes.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...