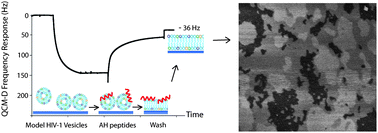
In this study, we present a technique to create complex, high cholesterol-containing supported lipid bilayers (SLBs) using α-helical (AH) peptide-induced vesicle fusion. Vesicles consisting of POPC : POPE : POPS : SM : Chol (9.35 : 19.25 : 8.25 : 18.15 : 45.00) were used to form a SLB that models the native composition of the human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) lipid envelope. In the absence of AH peptides, these biomimetic vesicles fail to form a complete SLB. We verified and characterized AH peptide-induced vesicle fusion by a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring, neutron reflectivity, and atomic force microscopy. Successful SLB formation entailed a characteristic frequency shift of −35.4 ± 0.8 Hz and a change in dissipation energy of 1.91 ± 0.23 × 10−6. Neutron reflectivity measurements determined the SLB thickness to be 49.9 +1.9−1.5 Å, and showed the SLB to be 100 +0.0−0.1% complete and void of residual AH peptide after washing. Atomic force microscopy imaging confirmed complete SLB formation and revealed three distinct domains with no visible defects. This vesicle fusion technique gives researchers access to a complex SLB composition with high cholesterol content and thus the ability to better recapitulate the native HIV-1 lipid membrane.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...