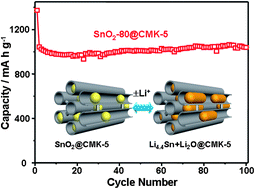
A tubular composite, including ultrafine SnO2 particles encapsulated in ordered tubular mesoporous carbon with thin walls and high pore volume, is fabricated through the in situ hydrolysis method. It is observed that up to 80 wt% of SnO2 particles with size between 4–5 nm are highly dispersed and homogeneously encapsulated in the mesopore channels and no bulky aggregates are visible. The tubular composite exhibits a considerably high reversible capacity of 978 mA h g−1 and a high initial efficiency of 71% at a current density of 200 mA g−1 between 0.005–3 V. Its reversible capacity even increases up to 1039 mA h g−1 after 100 cycles, which is much higher than the conventional theoretical capacity of SnO2 (782 mA h g−1), meanwhile, it also displays fast discharge/charge kinetics at a high current density of 1500 mA g−1. The excellent electrochemical performance is ascribed to its unique mesostructure by recruiting tubular mesoporous carbon with thin carbon walls (∼2 nm) and high pore volume (2.16 cm3 g−1). This tubular nanostructure provides confined nanospace for hosting immobilized ultrafine SnO2 with high loading, compensates volume expansion of SnO2, warrants efficient contact between nanoparticles and carbon matrix before and after Li+ insertion. We believe this special structure model might be extended for the fabrication of other cathode and anode electrode materials, to achieve high performance LIBs.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...