An enantio-selective chromatographic stationary phase for S-ibuprofen prepared by stoichiometric molecular imprinting
Abstract
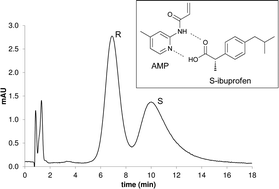
Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) against S-ibuprofen were synthesised using a tailor made functional monomer, 2-acrylamido-4-methylpyridine, following extensive pre-polymerisation studies of template–monomer complexation. An apparent association constant of 340 ± 22 M−1 was calculated that was subsequently corrected to account for dimerisation of ibuprofen (Kdim = 320 ± 95 M−1) resulting in an intrinsic association constant of 715 ± 16 M−1, consistent with previously reported values. Using the synthesised imprinted polymer as a stationary phase, complete resolution of a racemic mixture of ibuprofen was achieved in predominantly aqueous mobile phases. An imprinting factor of 10 was observed, and was found to be in agreement with the difference in the average number of binding sites between MIP and blank polymers, calculated by staircase frontal chromatography. The imprinted polymers exhibited enhanced selectivity for the templated drug over structurally related NSAIDs. When applied as sorbents in solid-phase extraction of ibuprofen from commercial tablets, urine and blood serum samples, recoveries up to 92.2% were achieved.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...