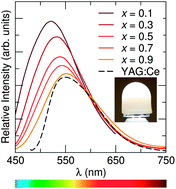
A near-UV excited, oxyfluoride phosphor solid solution Sr1.975Ce0.025Ba(AlO4F)1−x(SiO5)x has been developed for solid state white lighting applications. An examination of the host lattice, and the local structure around the Ce3+ activator ions through a combination of density functional theory, synchrotron X-ray and neutron powder diffraction and total scattering, and electron paramagnetic resonance, points to how chemical substitutions play a crucial role in tuning the optical properties of the phosphor. The maximum emission wavelength can be tuned from green (λem = 523 nm) to yellow (λem = 552 nm) by tuning the composition, x. Photoluminescent quantum yield is determined to be 70 ± 5% for some of the examples in the series. Excellent thermal properties were found for the x = 0.5 sample, with the photoluminescence intensity at 160 °C only decreased to 82% of its room temperature value. Phosphor-converted LED devices fabricated using an InGaN LED (λmax = 400 nm) exhibit high color rendering white light with Ra = 70 and a correlated color temperature near 7000 K. The value of Ra could be raised to 90 by the addition of a red component, and the correlated color temperature lowered to near 4000 K.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...