Phosphatase responsive peptide surfaces†
Abstract
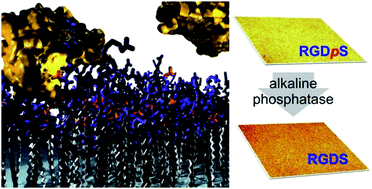
The development of interactive surfaces able to respond to biological cues is of interest for the development of next generation biomaterials. We report the design, synthesis and characterisation of an enzyme responsive

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...