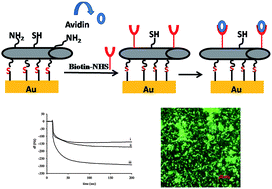
Functional gold surfaces are of great interest in the field of biosensors, since reactions taking place at such surfaces are easily detected and can be applied in numerous applications. Nanotubes (NTs) have been explored as modifying nanostructuration agents for quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) electrodes. Two goals must be achieved in this study. First, preparation of functional NTs which are able to bind to the gold surface; second, these NTs should have an additional functional group which will bind biological markers. Functional silica nanotubes (SNTs) have great potential in various applications due to their biocompatibility and ability to bind functional groups in a covalent manner using various silica based linkers. Although many publications deal with the introduction of functional groups onto the SNT surface, at present there are no reports in the literature regarding core–shell morphology with a functional polymer shell, which is covalently linked to SNTs. Furthermore, such functional core–shell SNTs can be further modified by other functional groups like amines or thiols by a 2nd step functionalization. This fact gives rise to an orthogonal nanocomposite (NC) that can be used as the essential modification component of QCM electrodes for the detection of biological markers.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...