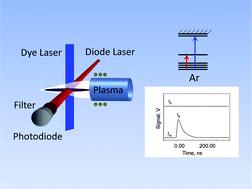
We report radially resolved relative number densities for argon metastable atoms recorded by bleaching absorbers in a short segment of the absorption path of a continuous wave diode laser with a pulsed dye laser. The densities were measured in the presence and in the absence of high concentrations of metallic species. Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Y, Cu, La, Nd, Sm, and Gd were introduced into the plasma to model a variety of matrix species. At a height of 12 mm above the load coil, all of the introduced matrix species with the exception of copper caused significant increases in the steady-state argon metastable atom density. To examine the relationship between the argon metastable atoms and analyte or matrix ions, we recorded transient changes in argon metastable density in response to pulsed laser radiation tuned to a resonance ionic line of a selected metal in the plasma. Saturation of the ionic resonance lines caused transient decreases in the argon metastable atom density on a nanosecond time scale. The response of the argon metastable atoms to excitation of metal species is too fast to be due to collisions between excited metal ions and argon metastable atoms. We attribute the observed responses to heating of the electrons by suprathermal inelastic collisions between electrons and excited metal ions, followed by enhanced collisional excitation by electrons of argon atoms in the 4s levels.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...