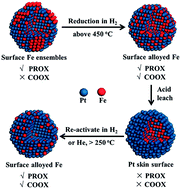
Surface Fe ensembles, surface alloyed Fe atoms, and subsurface Fe species have been identified at Pt surfaces on the basis of studies in Fe–Pt(111) model systems and supported Pt–Fe nanoparticles (NPs). The surface Fe ensemble changes to ferrous oxide and forms a highly active and stable “FeO-on-Pt” structure in preferential oxidation of CO in the presence of H2 (PROX), which, however, gets fully oxidized in CO oxidation in the absence of H2 (COOX) and becomes inactive in the reaction. The surface alloyed Fe remains stable under the H2-rich and O2-rich reaction conditions, which are active for both PROX and COOX reactions. Accordingly, highly efficient Pt–Fe catalysts for the PROX and COOX reactions can be prepared via mild reduction and/or acid leaching.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...