ZnO–Au nanohybrids by rapid microwave-assisted synthesis for CO oxidation†
Abstract
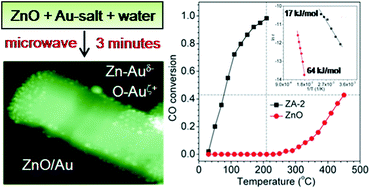
We present a green method for the synthesis of ZnO–Au hybrids using an ultrafast microwave-based technique. This method provides good control over the nucleation of the metal

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...