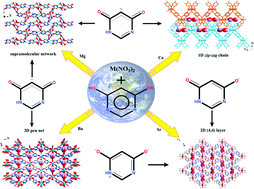
Nucleobase tautomers and their metal complexes have attracted considerable attention due to their fascinating architectures along with wide applications. In this paper, 4,6-dihydroxypyrimidine (H2DHP), an analogue of uracil and thymine, was employed to react with the vital elements of alkaline earth metals in an aqueous solution and lead to the formation of four novel complexes, [Mg(HDHP)2 (H2O)4] (1), [Ca(HDHP)2(H2O)3]n·nH2O (2), [Sr(HDHP)2(H2O)3]n·nH2O (3), and [Ba(HDHP)2(H2O)2]n·nH2O (4), which have been characterized by elemental analysis, IR, TG, UV-Vis, PL, powder and single-crystal X-ray diffraction and progressively evolve from zero-dimensional (0D) mononuclear, one-dimensional (1D) zig-zag double chain, two-dimensional (2D) double layer, to a three-dimensional (3D) porous network along with the increase of cation radii. This tendency in dimensionality follows salient crystal engineering principles and can be explained by considering factors such as hard–soft acid–base principles and cation radii. The deprotonated H2DHP ligand exhibits four new coordination modes, namely, O-monodentate (complex 1), N,O-chelating (complexes 2 and 3), O,O-bridging (complexes 2 and 3), and κ1O:κ2O-bridging mode (complex 4). Interestingly, the structural investigation indicates that the HDHP− monoanion shows three unusual types of tautomers, which are essential for the diagnosis of disease and investigation of medicine. Furthermore, the four complexes exhibit strong blue emission compared to free H2DHP ligand at room temperature and may be potential candidates for blue fluorescent biological materials used in organisms.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...