Migratory insertion reactions of nickel and palladium σ-alkyl complexes with a phosphinito-imine ligand†‡
Abstract
![[upper bond 1 start]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e010.gif) (CH2CMe2-o-C6
(CH2CMe2-o-C6![[upper bond 1 end]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e011.gif) H4)(P–N)], where P–N is the phosphinito-
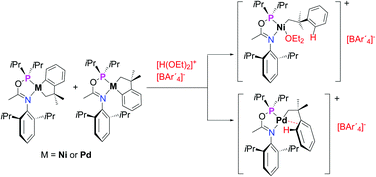
H4)(P–N)], where P–N is the phosphinito-![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N(2,6-C6H3(iPr)2. The protic acid [H(OEt2)(BAr′4)] (Ar′ = 3,5-C6H3(CF3)2) selectively cleaves one of the two σ metal–carbon bonds, affording cationic monoalkyl complexes. Nickel monoalkyls stabilized with Et2O or MeCN
N(2,6-C6H3(iPr)2. The protic acid [H(OEt2)(BAr′4)] (Ar′ = 3,5-C6H3(CF3)2) selectively cleaves one of the two σ metal–carbon bonds, affording cationic monoalkyl complexes. Nickel monoalkyls stabilized with Et2O or MeCN
- This article is part of the themed collection: In Celebration of David Cole-Hamilton's Career in Chemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...