Alignment of electronic energy levels at electrochemical interfaces
Abstract
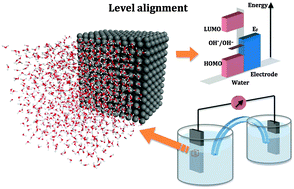
The position of electronic energy levels in a phase depends on the surface potentials at its boundaries. Bringing two phases in contact at an interface will alter the surface potentials shifting the energy levels relative to each other. Calculating such shifts for electrochemical interfaces requires a combination of methods from computational surface science and physical chemistry. The problem is closely related to the computation of potentials of electrochemically inactive electrodes. These so-called ideally polarizable interfaces are impossible to cross for electrons. In this perspective we review two density functional theory based methods that have been developed for this purpose, the workfunction method and the hydrogen insertion method. The key expressions of the two methods are derived from the formal theory of absolute electrode potentials. As an illustration of the workfunction method we review the computation of the potential of zero charge of the Pt(111)–water interface as recently published by a number of groups. The example of the hydrogen insertion method is from our own work on the rutile TiO2(110)–water interface at the point of zero proton charge. The calculations are summarized in level diagrams aligning the electronic energy levels of the solid electrode (Fermi level of the metal, valence band maximum and conduction band minimum of the semiconductor) to the band edges of liquid water and the standard potential for the reduction of the hydroxyl radical. All potentials are calculated at the same level of density functional theory using the standard hydrogen electrode as common energy reference. Comparison to experiment identifies the treatment of the valence band of water as a potentially dangerous source of error for application to electrocatalysis and photocatalysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...