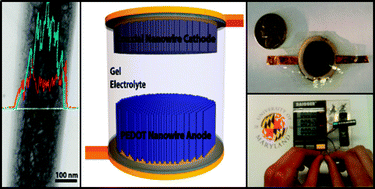
Flexible electronics such as wearable electronic clothing, paper-like electronic devices, and flexible biomedical diagnostic devices are expected to be commercialized in the near future. Flexible energy storage will be needed to power these devices. Supercapacitor devices based on freestanding nanowire arrays are promising high power sources for these flexible electronics. Electrodes for these supercapacitor devices consisting of heterogeneous coaxial nanowires of poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT)-shell and MnO2-core materials have been shown in a half cell system to have improved capacitance and rate capabilities when compared to their pure nanomaterials; however, their performance in a full cell system has not been fully investigated. Herein, these coaxial nanowires are tested in both a symmetric and an asymmetric (utilizing a PEDOT nanowire anode) full cell configuration in the aspect of charge storage, charge rate, and flexibility without using any carbon additives and polymer binders. It is found that the asymmetric cell outperforms the symmetric cell in terms of energy density, rate capability, and cycle ability. The asymmetric device's electrode materials display an energy density of 9.8 Wh/kg even at a high power density of 850 W kg−1. This device is highly flexible and shows fast charging and discharging while still maintaining 86% of its energy density even under a highly flexed state. The total device is shown to have a total capacitance of 0.26 F at a maximum voltage of 1.7 V, which is capable of providing enough energy to power small portable devices.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...