Controlled perturbation of the thermodynamic equilibrium by microfluidic separation of porphyrin-based aggregates in a multi-component self-assembling system†
Abstract
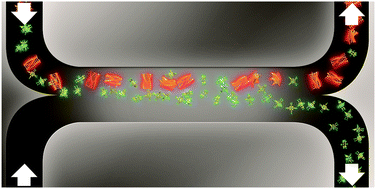
In a microfluidic H-cell, a multi-component self-assembled system is brought out-of-equilibrium by changing the bimodal composition of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...