Hypomethylation of fetal brain genomic DNA in neural tube defects determined by a new liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) method
Abstract
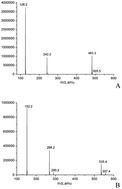
Neural tube defects (NTDs) are associated with significant infant morbidity and mortality. Detection of alterations in DNA methylation might provide evidence for an epigenetic mechanism in some NTDs cases. We developed a sensitive LC–MS/MS method for the quantification of global DNA methylation in low quantity samples of embryonic tissue. The limit of detection was 0.5 × 10−15 mol for 5-methyl-2′-deoxycytidine (5mdC) and the assay was linear from 1 × 10−14 mol to 1 × 10−11 mol for 5mdC with DNA input between 1 ng and 1000 ng. The calibration curve ranged from 1% to 10% with a correlation coefficient (r2) of 0.998 for methylation levels ranging from 2% to 7% of the mammalian genome. The intra-day precision was 2.19% to 7.73% and the inter-day precision was 0.87% to 4.33%, with an overall accuracy between 97.30% and 107.66%. Following method validation, we applied this method for the first time to assess global DNA methylation in fetal tissue from confirmed anencephalus and spina bifida cases. Brain tissue from these NTDs cases showed DNA hypomethylation compared to control samples, while no differences were found in skin tissue. Results from statistical analysis demonstrated that the global DNA methylation level was independent of gender. The methylation analysis suggested that hypomethylation was associated with NTDs, implicating a possible epigenetic mechanism in the pathogenesis of anencephalus and spina bifida.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...