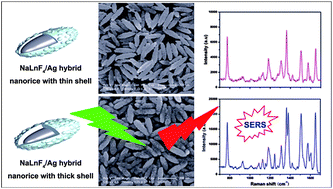
This paper reports the synthesis of a new class of NaLnF4–Ag (Ln = Nd, Sm, Eu, Tb, Ho) hybrid nanorice and its application as a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate in chemical analyses. Rice-shaped NaLnF4 nanoparticles as templates are prepared by a modified hydrothermal method. Then, the NaLnF4 nanorice particles are decorated with Ag nanoparticles by magnetron sputtering method to form NaLnF4–Ag hybrid nanostructures. The high-density Ag nanogaps on NaLnF4 can be obtained by the prolonging sputtering times or increasing the sputtering powers. These nanogaps can serve as Raman ‘hot spots’, leading to dramatic enhancement of the Raman signal. The NaLnF4–Ag hybrid nanorice is found to be robust and is an efficient SERS substrate for the vibrational spectroscopic characterization of molecular adsorbates; the Raman enhancement factor of Rhodamine 6G (R6G) absorbed on NaLnF4–Ag nanorice is estimated to be about 1013. Since the produced NaLnF4–Ag hybrid nanorice particles are firmly fastened on a silicon wafer, they can serve as universal SERS substrates to detect target analytes. We also evaluate their SERS performances using 4-mercaptopyridine (Mpy), and 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (MBA) molecules, and the detection limit for Mpy and MBA is as low as 10−12 M and 10−10 M, respectively, which meets the requirements of the ultratrace detection of analytes. This simple and highly efficient approach to the large-scale synthesis of NaLnF4–Ag nanorice with high SERS activity and sensitivity makes it a perfect choice for practical SERS detection applications.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...