Surface instability of soft solids under strain
Abstract
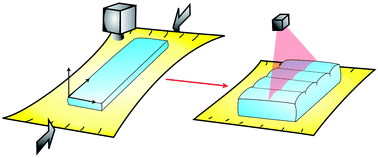
Using a uniaxial deformation setup, we show that the free surface of an homogeneous elastic material is unstable under compression: parallel grooves nucleate orthogonally to the direction of compression when a characteristic stretch ratio a* is reached. We measure experimentally the variation of a* as well as the wavelength of the grooves as a function of the thickness h0 of the material. All data collapse on single curves when normalizing h0 by a characteristic length which is the ratio of the surface tension to the shear modulus of the material. This length scale acts as a regularization parameter for the system. We introduce a theoretical model that captures well the features of the instability. The observed nucleation-like process for the grooves development suggests that the instability is subcritical.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...