Bouncing bubble on a liquid/gas interface resting or vibrating
Abstract
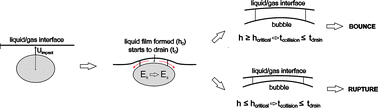
The bouncing of air bubbles of about 1 mm in diameter on an air/oil interface is reported. We compare the behavior of the bubble when the interface is at rest or when it is vibrated. The results obtained for the interface at rest allowed extracting the key parameter responsible for the outcome of the bubble collision, i.e. bounce or coalescence (bubble rupture). This parameter is the deformation of the bubble. When the bubble deformation is sufficient (according to the oil viscosity and to the bubble velocity and size), the bubble bounces because the intervening oil film has a large radius and the bubble–interface contact time is much shorter than the time needed for the film drainage to its critical thickness of rupture. This hypothesis is confirmed by the experiments of the bubble collisions with vertically vibrated air/oil interface. It was shown that it is possible to significantly increase the bubble lifetime: the bubble bounces at the interface when the interface is vibrated, and this occurs when the vibration amplitude is above a threshold. The amplitude threshold depends on the frequency, on the size of the bubble and on the viscosity of the surrounding oil. For bouncing, the vibrated interface must provide enough energy to the bubble to deform in such a way that the drainage characteristic time of the oil film becomes longer than the contact time between the bubble and the interface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...