A novel ubiquitin binding mode in the S. cerevisiaetranslesion synthesis DNA polymerase η†
Abstract
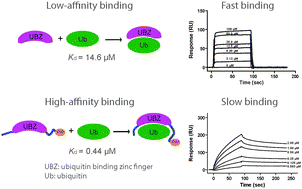
The ubiquitin binding zinc finger (UBZ) domain in the C-terminal portion of Polη has been found to interact with ubiquitin. However, the affinity between the Polη UBZ and ubiquitin was shown to be low with a previously reported Kd of 73–81 μM. This low-affinity binding between Polη UBZ and ubiquitin has been difficult to reconcile with its presumed role in translesion synthesis as suggested by genetic and cell biology studies. In this work, we constructed a minimal S. cerevisiae Polη UBZ domain and probed the Polη UBZ-ubiquitin interaction using a surface plasmon resonance (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...