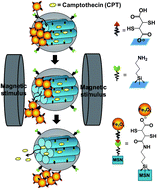
In this study, a novel nanocarrier (MSN@Fe3O4) is constructed using a facile technology by capping mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) with monodispersed Fe3O4 nanoparticles through chemical bonding. The chemical links provide adhesion, which permits the magnetic nanoparticles, as nano-caps, to efficiently cover the mesoporous pores on the mesoporous silica matrix and be tightly bonded with the matrix surface. Without magnetic stimulus, none or only a negligible amount of the drug can be released from the MSN@Fe3O4. However, when subjected to an external controllable magnetic field, a quantity of nano-caps can be remotely and precisely removed, giving tunable release profiles for an anticancer drug, (S)-(+)-camptothecin (CPT), with various dosages depending upon the strength and time period of magnetic induction. The transverse relaxivity (r2) of the MSN@Fe3O4 nanocarriers was measured to be about 121.57 s−1mM−1Fe, which is larger than that for the reported mesoporous silica nanoparticles decorated with magnetite nanocrystals. Therefore, MSN@Fe3O4 nanocarriers could perform well as T2- type MR contrast enhancement agents for cell or molecular imaging. In addition, the MSN@Fe3O4 nanocarriers also demonstrate fairly high cell uptake efficiency. Together with its versatile magnetic manipulation, this new type of MSN@Fe3O4 nanosystem can be considered as a new class of multifunctional nanodevice, with combined tunable drug release and nanoimaging modalities for a variety of biomedical uses.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...