Synthesis of highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles using l-ascorbic acid
Abstract
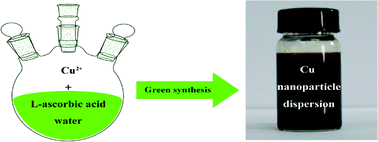
Highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles with an average particle size less than 2 nm were synthesized using a straightforward, cost-effective, and green method. Nontoxic

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...