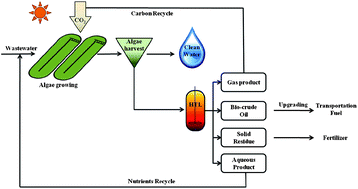
Microalgae are considered to be a promising alternative feedstock for next generation biofuels because of their rapid photosynthetic growth rates and less impact on land-use for food production compared with grain and other lignocellulosic biomass. In this study, a fast-growing, low-lipid, high-protein microalga species, Chlorella pyrenoidosa, was converted via hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) into four products: bio-crude oil, aqueous product, gaseous product, and solid residue. The effects of operating conditions (reaction temperature and retention time) on the distributions of carbon and nitrogen in HTL products were quantified. Carbon recovery (CR), nitrogen recovery (NR) and energy recovery in the bio-crude oil fraction generally increased with the increase of reaction temperature as well as the retention time. The highest energy recovery of bio-crude oil was 65.4%, obtained at 280 °C with 120 min retention time. Both carbon and nitrogen tended to preferentially accumulate in the HTL bio-crude oil products as temperature and retention time increased, but the opposite was true for the solid residual product. The NR values of HTL aqueous product also increased with reaction temperature and retention time. 65–70% of nitrogen and 35–40% of carbon in the original material were converted into water soluble compounds when reaction temperature was higher than 220 °C and retention time was longer than 10 min. The CR of gas was less than 10% and is primarily present in the form of carbon dioxide. This study also introduces a novel treatment process (Environment-Enhancing Energy) that integrates algal growth for wastewater treatment with HTL of algal biomass, which provides synergistic recycling of carbon dioxide from the HTL gaseous product and the nutrients from HTL aqueous product to support multiple stages of algae production.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...