Binding and photodissociation of CO in iron(ii) complexes for application in positron emission tomography (PET) radiolabelling†
Abstract
(R-DAB)FeI2 complexes containing bidentate ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH–CH
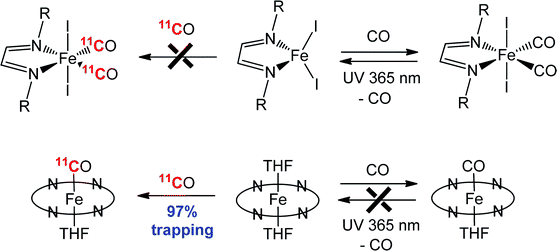
CH–CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NR; R = iPr, c-C6H11) have been investigated for their ability to react with carbon monoxide to form iron(II) dicarbonyl complexes, (R-DAB)FeI2(CO)2. Solution
NR; R = iPr, c-C6H11) have been investigated for their ability to react with carbon monoxide to form iron(II) dicarbonyl complexes, (R-DAB)FeI2(CO)2. Solution
- This article is part of the themed collection: Radiopharmaceuticals for imaging and therapy
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...