We developed convenient synthetic routes for the preparation of para-benzene disulfonic acid (H2BDS) and its tetrachloro (H2BDSCl4) and tetrafluoro (H2BDSF4) derivatives. The reaction of these acids with zinc nitrate in DMF led to single crystals of [Zn(BDS)(DMF)2] (triclinic, P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) , Z = 2, a = 976.62(4), b = 986.85(4), c = 1014.40(4), α = 69.106(2)°, β = 68.746(2)°, γ = 86.295(2)°, wR2 = 0.0627), [Zn(BDSCl4)(DMF)4] (triclinic, P
, Z = 2, a = 976.62(4), b = 986.85(4), c = 1014.40(4), α = 69.106(2)°, β = 68.746(2)°, γ = 86.295(2)°, wR2 = 0.0627), [Zn(BDSCl4)(DMF)4] (triclinic, P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) , Z = 1, a = 831.5(1), b = 905.2(1), c = 989.6(1), α = 90.44(2)°, β = 91.41 (2)°, γ = 106.72(2)°, wR2 = 0.0635), and [Zn(BDSF4)(DMF)4] (monoclinic, P21/c, Z = 2, a = 889.01(3), b = 968.91(3), c = 1633.07(5) pm, β = 106.524(2)°, wR2 = 0.0948). While [Zn(BDS)(DMF)2] exhibits a layer structure, the disulfonate linkers connect the zinc ions into chains in the crystal structures of [Zn(BDSCl4)(DMF)4] and [Zn(BDSF4)(DMF)4]. Thermoanalytical investigations revealed that desolvation of the compounds occurs in a temperature range between 100 and 200 °C. The solvent free sulfonates show remarkably high stabilities, [Zn(BDS)(DMF)2] is stable up to nearly 600 °C. The halogenated acids were also used to prepare copper salts from aqueous solutions and Cu2(OH)2(CO3) (malachite) as a copper source. The crystal structure of [Cu(H2O)6](BDSF4) (triclinic, P
, Z = 1, a = 831.5(1), b = 905.2(1), c = 989.6(1), α = 90.44(2)°, β = 91.41 (2)°, γ = 106.72(2)°, wR2 = 0.0635), and [Zn(BDSF4)(DMF)4] (monoclinic, P21/c, Z = 2, a = 889.01(3), b = 968.91(3), c = 1633.07(5) pm, β = 106.524(2)°, wR2 = 0.0948). While [Zn(BDS)(DMF)2] exhibits a layer structure, the disulfonate linkers connect the zinc ions into chains in the crystal structures of [Zn(BDSCl4)(DMF)4] and [Zn(BDSF4)(DMF)4]. Thermoanalytical investigations revealed that desolvation of the compounds occurs in a temperature range between 100 and 200 °C. The solvent free sulfonates show remarkably high stabilities, [Zn(BDS)(DMF)2] is stable up to nearly 600 °C. The halogenated acids were also used to prepare copper salts from aqueous solutions and Cu2(OH)2(CO3) (malachite) as a copper source. The crystal structure of [Cu(H2O)6](BDSF4) (triclinic, P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) , Z = 1, a = 510.45(2), b = 744.68(3), c = 1077.77(4) pm, α = 85.627 (2)°, β = 77.449 (2)°, γ = 76.015 (2)°) exhibits complex cations and uncoordinated sulfonate anions, while in [Cu(BDSCl4)(H2O)4] (orthorhombic, Pnma, Z = 4, a = 721.27(2), b = 2147.81(6), c = 979.42(3) pm) the Cu2+ ions are linked to infinite chains in the crystal structure. The most interesting structural feature of [Cu(BDSCl4)(H2O)4] is the significant deviation from planarity of the disulfonate dianion. Theoretical investigations revealed that a boat conformation is favoured due to steric hindrance in cases where a syn coordination of the sulfonate groups occurs. The thermal behaviour of the copper compounds was also investigated by DTA/TG measurements and X-ray powder diffraction.
, Z = 1, a = 510.45(2), b = 744.68(3), c = 1077.77(4) pm, α = 85.627 (2)°, β = 77.449 (2)°, γ = 76.015 (2)°) exhibits complex cations and uncoordinated sulfonate anions, while in [Cu(BDSCl4)(H2O)4] (orthorhombic, Pnma, Z = 4, a = 721.27(2), b = 2147.81(6), c = 979.42(3) pm) the Cu2+ ions are linked to infinite chains in the crystal structure. The most interesting structural feature of [Cu(BDSCl4)(H2O)4] is the significant deviation from planarity of the disulfonate dianion. Theoretical investigations revealed that a boat conformation is favoured due to steric hindrance in cases where a syn coordination of the sulfonate groups occurs. The thermal behaviour of the copper compounds was also investigated by DTA/TG measurements and X-ray powder diffraction.
![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) , Z = 2, a = 976.62(4), b = 986.85(4), c = 1014.40(4), α = 69.106(2)°, β = 68.746(2)°, γ = 86.295(2)°, wR2 = 0.0627), [Zn(BDSCl4)(DMF)4] (triclinic, P
, Z = 2, a = 976.62(4), b = 986.85(4), c = 1014.40(4), α = 69.106(2)°, β = 68.746(2)°, γ = 86.295(2)°, wR2 = 0.0627), [Zn(BDSCl4)(DMF)4] (triclinic, P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) , Z = 1, a = 831.5(1), b = 905.2(1), c = 989.6(1), α = 90.44(2)°, β = 91.41 (2)°, γ = 106.72(2)°, wR2 = 0.0635), and [Zn(BDSF4)(DMF)4] (monoclinic, P21/c, Z = 2, a = 889.01(3), b = 968.91(3), c = 1633.07(5) pm, β = 106.524(2)°, wR2 = 0.0948). While [Zn(BDS)(DMF)2] exhibits a layer structure, the disulfonate linkers connect the
, Z = 1, a = 831.5(1), b = 905.2(1), c = 989.6(1), α = 90.44(2)°, β = 91.41 (2)°, γ = 106.72(2)°, wR2 = 0.0635), and [Zn(BDSF4)(DMF)4] (monoclinic, P21/c, Z = 2, a = 889.01(3), b = 968.91(3), c = 1633.07(5) pm, β = 106.524(2)°, wR2 = 0.0948). While [Zn(BDS)(DMF)2] exhibits a layer structure, the disulfonate linkers connect the ![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) , Z = 1, a = 510.45(2), b = 744.68(3), c = 1077.77(4) pm, α = 85.627 (2)°, β = 77.449 (2)°, γ = 76.015 (2)°) exhibits complex
, Z = 1, a = 510.45(2), b = 744.68(3), c = 1077.77(4) pm, α = 85.627 (2)°, β = 77.449 (2)°, γ = 76.015 (2)°) exhibits complex 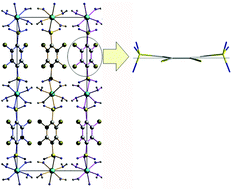

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...