Protonation states in a cobalt-oxidecatalyst for water oxidation: fine comparison of ab initio molecular dynamics and X-ray absorption spectroscopy results†
Abstract
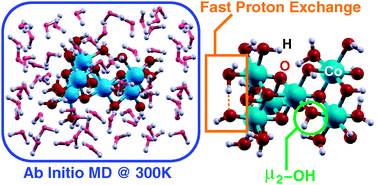
Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations of a recently proposed cobalt-based

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...