Halogen bonded complexes between volatile anaesthetics (chloroform, halothane, enflurane, isoflurane) and formaldehyde: a theoretical study
Abstract
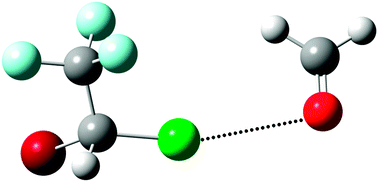
The structures and intermolecular interactions in the
* Corresponding authors
a
Faculty of Chemistry, Wrocław University of Technology, Wybrzeże Wyspiańskiego 27, 50-370 Wrocław, Poland
E-mail:
wiktor.zierkiewicz@pwr.wroc.pl
Fax: +48 71-320-4360
Tel: +48 71-320-3455
b Faculty of Chemistry, University of Wroclaw, F. Joliot-Curie 14, 50-383 Wroclaw, Poland
c Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic and Center for Biomolecules and Complex Molecular Systems, 166 10 Praha 6, Czech Republic
d Department of Physical Chemistry, Palacky University, 771 46 Olomouc, Czech Republic
The structures and intermolecular interactions in the

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
W. Zierkiewicz, R. Wieczorek, P. Hobza and D. Michalska, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011, 13, 5105 DOI: 10.1039/C0CP02085K
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
