Affinity of hydroxyapatite (001) and (010) surfaces to formic and alendronic acids: a quantum-mechanical and infrared study†
Abstract
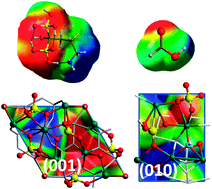
The affinity of the (001) and of the water reacted (010)WR hydroxyapatite surfaces towards formic and alendronic acids is studied with density functional theory (PBE functional) using periodic boundary conditions based on Gaussian basis set. Structures, energetic of the adsorption and vibrational features of the adsorbates are computed in order to understand at the atomic level both the cariogenic processes (for the formic acid) and the features of anti-osteoporosis ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching bands have been found to be in excellent agreement with the quantum mechanical simulations. For
O stretching bands have been found to be in excellent agreement with the quantum mechanical simulations. For

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...