Tissue imprint imaging by desorption electrospray ionizationmass spectrometry
Abstract
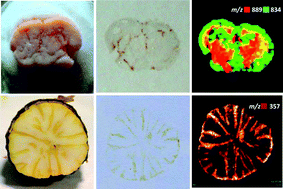
Cross-sections of Myristica malabarica (Lam) seed and mouse brain tissue were imprinted on such ordinary surfaces as printer paper and TLC plates, and successfully imaged by

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...