Loose packings of frictional spheres†
Abstract
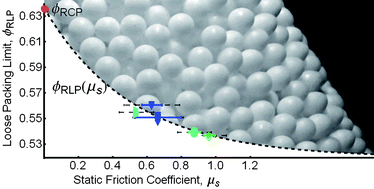
We have produced loose packings of cohesionless, frictional spheres by sequential deposition of highly-spherical, monodisperse particles through a fluid. By varying the properties of the fluid and the particles, we have identified the Stokes number (St)—rather than the buoyancy of the particles in the fluid—as the parameter controlling the approach to the loose packing limit. The loose packing limit is attained at a threshold value of St at which the kinetic energy of a particle impinging on the packing is fully dissipated by the fluid. Thus, for cohesionless particles, the dynamics of the deposition process, rather than the stability of the static packing, defines the random loose packing limit. We have made direct measurements of the interparticle friction in the fluid, and present an experimental measurement of the loose packing volume fraction,
- This article is part of the themed collection: Granular and jammed materials

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...