Synthesis of thermoresponsive phenyl- and naphthyl-terminated poly(NIPAM) derivatives using RAFT and their complexation with cyclobis(paraquat-p-phenylene) derivatives in water†
Abstract
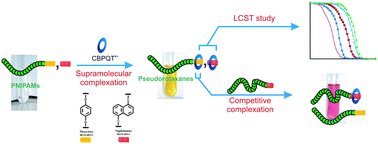
A series of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)s (poly(NIPAM)s) have been synthesized via reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT)

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...