Abstract
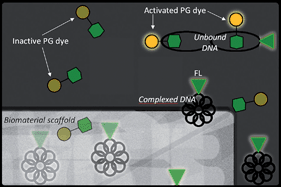
Quantification of eluted nucleic acids is a critical parameter in characterizing biomaterial based gene-delivery systems. The most commonly used method is to assay samples with an intercalating fluorescent dye such as PicoGreen®. However, this technique was developed for unbound DNA and the current trend in gene delivery is to condense DNA with transfection reagents, which interfere with intercalation. Here, for the first time, the DNA was permanently labeled with the fluorescent dye Cy5 prior to complexation, an alternative technique hypothesized to allow quantification of both bound and unbound DNA. A comparison of the two methods was performed by quantifying the elution of six different varieties of DNA complexes from a model biomaterial (collagen) scaffold. After seven days of elution, the PicoGreen® assay only allowed detection of three types of complexes (those formed using Lipofectin™ and two synthesised copolymers). However, the Cy5 fluorescent labeling technique enabled detection of all six varieties including those formed via common transfection agents poly(ethylene imine), poly-L-lysine and SuperFect™. This allowed reliable quantification of the elution of all these complexes from the collagen scaffold. Thus, while intercalating dyes may be effective and reliable for detecting double-stranded, unbound DNA, the technique described in this work allowed reliable quantification of DNA independent of complexation state.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...