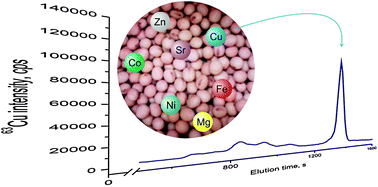
Transgenic and non-transgenic soybean seeds were compared in terms of total element concentrations, behavior of elements during sequential extraction fractionation and element bioaccessibility using an in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion. The analysis were carried out by ICP-sector field-MS or size-exclusion ICP-MS (25 elements in concentrations varying from ng g−1 to the % level). It seems that transgenic and non-transgenic soybean seeds exhibit statistically significant differences in concentrations of Cu, Fe and Sr, which are also reflected by element contents in water extracts and residues. Additionally, contributions of bioaccessible fractions of Cu, Fe and other elements (Mn, S, Zn) for transgenic soybean seeds appear to be larger than those found in non-transgenic soybean seeds.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...