Use of magnetic field for addressing, grafting onto support and actuating permanent magnetic filaments applied to enhanced biodetection†
Abstract
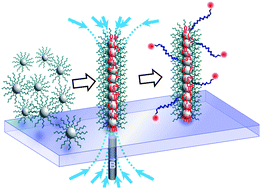
A simple method combining magnetic field and microparticles has been designed for assembling, locating and grafting permanent

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...