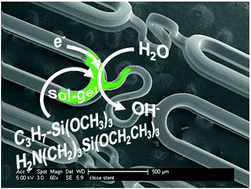
The electrochemically assisted codeposition of sol–gel thin films on stainless steel is described. Specifically, electrodeposition of films based on aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTS), and its codeposition with propyltrimethoxysilane (PrTMOS) and phenyltrimethoxysilane (PhTMOS) has been accomplished by applying negative potentials. The latter increases the concentration of hydroxyl ions on the stainless steel surface and thus catalyzes the condensation and deposition of the sol–gel films. The films were characterized by profilometry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), alternating current voltammetry (ACV), goniometry, atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). AFM and SEM analysis of codeposited APTS ∶ PrTMOS films disclosed the structural changes induced by altering the deposition solution composition and the applied potential. Codeposited APTS ∶ PhTMOS did not show any structural differences from their electrodeposited homopolymers, while Nano Scratch Test clearly revealed the changes in the elastic and adhesion properties, suggesting the formation of an APTS ∶ PhTMOS composite. EIS of the films showed good resistance towards penetration of hydrophilic species, such as hexacyanoferrate. ACV measurements of the homo and codeposits showed the decrease of the interfacial capacity as a result of the electrochemical deposition. In essence, controllable sol–gel films with tunable chemical and physical properties based on controlling the combination of the precursors, pH and electrochemical properties can be electrodeposited on conducting surfaces. The application of this approach has been demonstrated by coating a stainless steel coronary stent.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...