Modelling nano-clusters and nucleation
Abstract
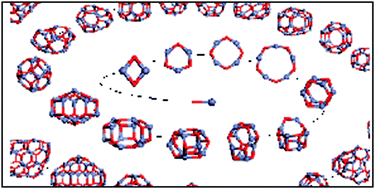
We review the growing role of computational techniques in modelling the structures and properties of nano-particulate oxides and sulphides. We describe the main methods employed, including those based on both electronic structure and interatomic potential approaches. Particular attention is paid to the techniques used in searching for global minima in the energy landscape defined by the nano-particle

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...