The aqueous photosensitized degradation of butylparaben
Abstract
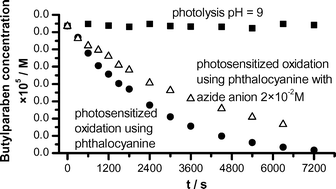
The photosensitized oxidation of butyl p-hydroxybenzoate (butylparaben, BP), the endocrine disrupting compound, in aqueous solution using rose bengal (RB) and aluminium phthalocyanine chloride tetrasulfonic acid (PC) as sensitizers was examined. A xenon lamp simulating solar radiation was used as a light source. The influence of pH of the reaction mixture, oxygen content, irradiation intensity and initial sensitizers and BP concentration on the reaction rate was studied. Based on the kinetic model, the rate constants of singlet oxygen quenching and reaction with BP as well as the rate constant of excited sensitizer quenching by BP were determined.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...