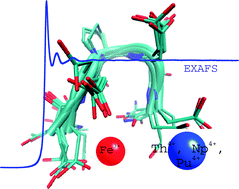
Although there is a tremendous volume of data available on the interaction of actinides with living organisms as plants, nearly all the studies are limited to macroscopic or physiological measurements with no specific information at the molecular level. Peptides allow the study of complex coordination chemistry, as that involving actinide(IV) and proteins, without the intricacy of tertiary structure properties. For that purpose, a linear pentapeptide, acetyl–diaspartyl–prolyl–diaspartyl–amide (Ac–Asp–Asp–Pro–Asp–Asp–NH2, denoted PP1 in this report), was synthesized and investigated as a potential chelating ligand of thorium(IV), neptunium(IV) and/or plutonium(IV) cations. Comparison with the biological relevant iron(III) cation is also provided. Noteworthy, PP1 was able to prevent Np(IV) from hydrolysis into an insoluble precipitate. Spectrophotometry, 13C NMR and EXAFS at the iron K edge and actinide L3 edges were used to probe the cation coordination sphere and better describe the cation–peptide interaction. The complexes were found to be polynuclear with oxo or hydroxo bridged cations, Fe(III) forming a binuclear complex, Th(IV), Np(IV) or Pu(IV) forming a polynuclear complex with higher nuclearities.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...