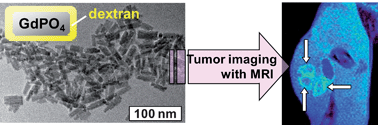
Tumor detection is of great clinical interest. It is known that solid tumors have unique vascular pathophysiological features summarized under the term “enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect”, which induces the accumulation and prolonged retention of macromolecules from the blood into the tumor. We therefore have designed and synthesized dextran coated paramagnetic gadolinium phosphate nanoparticles (PGP/dextran) as a new magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent. The main features of this new material are: (i) characteristics of a positive contrast agent providing higher imaging resolution, (ii) size of several tens of nanometres to accumulate and to be retained into tumors, and (iii) highly biocompatible dextran coating to prevent the rapid elimination from the blood stream. In this article, we describe the results of pharmacokinetic studies, toxicity tests, and MR imaging experiments to visualize tumors using PGP/dextran, and compare them to the clinically used contrast agent Magnevist®. Relying on the EPR effect, tumors in a rabbit were successfully visualized on conventional T1-weighted MR images using the particulate and positive PGP/dextran with only 1/10 of the applied dose compared to Magnevist®. This efficient visualization of a tumor is the result of the comprehensive features of PGP/dextran, having adequate characteristics of a positive contrast agent for MRI, a significantly long plasma half-life and a high biocompatibility. PGP/dextran could be used as a tumor specific contrast agent and as a vehicle to deliver drugs to a tumor.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...