Direct growth of SnO2nanorod array electrodes for lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
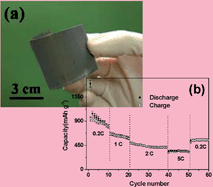
SnO2nanorod arrays have been prepared on large-area flexible metallic substrates (Fe–Co–Ni alloy and Ni foil) via a hydrothermal process for the first time and have been demonstrated as a high-performance anode material for lithium ion batteries. Electrochemical behavior is found to depend crucially on the structural parameters of the array. An array consisting of SnO2nanorods of average 60 nm in diameter and 670 nm in length delivers a reversible capacity of as high as 580 mAh g−1 after 100 cycles (at 0.1C) and shows excellent rate capability (350 mAh g−1 at the 5C rate). Structural disintegration and agglomeration were not observed for SnO2 arrays even after 50 cycles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...