Bimetallic complexes based on carboxylate and xanthateligands: Synthesis and electrochemical investigations†
Abstract
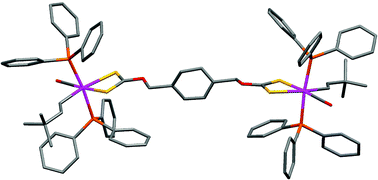
The homobimetallic ruthenium(II) and osmium(II) complexes [{RuR(CO)(PPh3)2}2(S2COCH2C6H4CH2OCS2)] (R = CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHBut, CH
CHBut, CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHC6H4Me-4, C(C
CHC6H4Me-4, C(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)
CPh)![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHPh, CH
CHPh, CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCPh2OH) and [{Os(CH
CHCPh2OH) and [{Os(CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHC6H4Me-4)(CO)(PPh3)2}2(S2COCH2C6H4CH2OCS2)] form readily from the reactions of [MRCl(CO)(BTD)(PPh3)2] (M = Ru or Os; BTD =
CHC6H4Me-4)(CO)(PPh3)2}2(S2COCH2C6H4CH2OCS2)] form readily from the reactions of [MRCl(CO)(BTD)(PPh3)2] (M = Ru or Os; BTD = ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHBut, CH
CHBut, CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHC6H4Me-4, C(C
CHC6H4Me-4, C(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)
CPh)![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHPh) are obtained by treatment of [RuRCl(CO)(BTD)(PPh3)2] with
CHPh) are obtained by treatment of [RuRCl(CO)(BTD)(PPh3)2] with ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHC6H4Me-4)(CO)(PPh3)2}2(O2CC6H4CH2OCS2)] forms from the sequential treatment of [Ru(CH
CHC6H4Me-4)(CO)(PPh3)2}2(O2CC6H4CH2OCS2)] forms from the sequential treatment of [Ru(CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHC6H4Me-4){O2CC6H4(CH2OH)-4}(CO)(PPh3)2] with base, CS2 and [Ru(CH
CHC6H4Me-4){O2CC6H4(CH2OH)-4}(CO)(PPh3)2] with base, CS2 and [Ru(CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHC6H4Me-4)Cl(CO)(BTD)(PPh3)2]. The new mixed-donor xanthate-carboxylate
CHC6H4Me-4)Cl(CO)(BTD)(PPh3)2]. The new mixed-donor xanthate-carboxylate ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHC6H4Me-4)Cl(BTD)(CO)(PPh3)2] or cis-[RuCl2(dppm)2] to yield [{(dppm)2Ru}2(O2CC6H4CH2OCS2)]2+ or [{Ru(CH
CHC6H4Me-4)Cl(BTD)(CO)(PPh3)2] or cis-[RuCl2(dppm)2] to yield [{(dppm)2Ru}2(O2CC6H4CH2OCS2)]2+ or [{Ru(CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHC6H4Me-4)(CO)(PPh3)2}2(O2CC6H4CH2OCS2)], respectively. Electrochemical experiments are also reported in which communication between the metal centres is investigated.
CHC6H4Me-4)(CO)(PPh3)2}2(O2CC6H4CH2OCS2)], respectively. Electrochemical experiments are also reported in which communication between the metal centres is investigated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...