Experimental and theoretical investigations of CB8−: towards rational design of hypercoordinated planar chemical species
Abstract
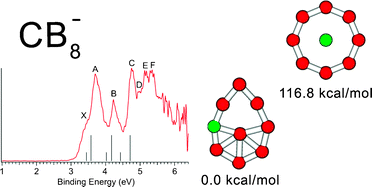
We demonstrated in our joint photoelectron spectroscopic and ab initio study that wheel-type structures with a boron ring are not appropriate for designing planar molecules with a hypercoordinate central carbon based on the example of CB8, and CB8−clusters. We presented a chemical bonding model, derived from the adaptive natural density partitioning analysis, capable of rationalizing and predicting planar structures either with a boron ring or with a carbon atom occupying the central hypercoordinate position. According to our chemical bonding model, in the wheel-type structures the central atom is involved in delocalized bonding, while peripheral atoms are involved in both delocalized bonding and two-center two-electron (2c–2e) σ-bonding. Since carbon is more electronegative than boron it favors peripheral positions where it can participate in 2c–2e σ-bonding. To design a chemical species with a central hypercoordinate carbon atom, one should consider electropositive

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...